
32.44 - 20 log f c/ 1MHz - 20 log d / 1km, where the loss is found in dB.įree Space Loss Calculator Input parameters: Show that the path loss L between two isotropic antennas ( G R = 1, G t = 1) can be If you wish to enter distance in kilometer, check the calculator here.
#Freespace loss calculator free
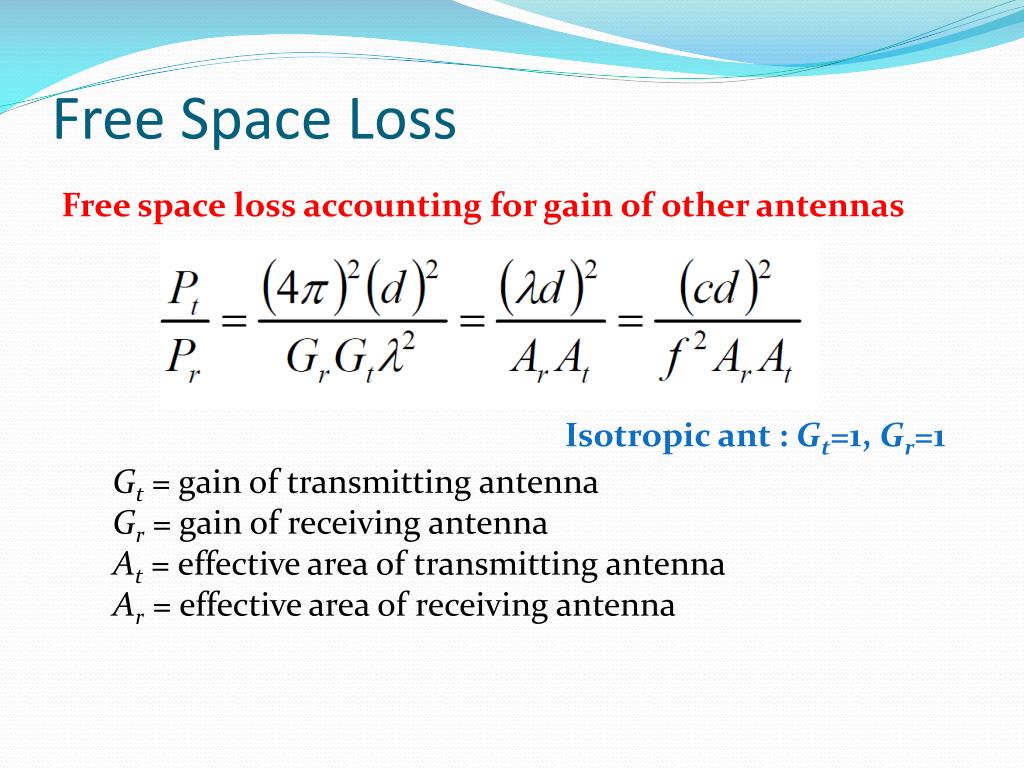
Expressed in dB, the received power isĮngineers speak about a "20 log d" path loss law. Free Space Loss (dB) 36.6 + 20 x Log (Frequency (MHz) x Distance (Miles)) Freq in MHz. Free Space Path Loss assumes the space between the two antennas is an obstruction free, line-of-sight straight path through the air. The product G t p T is called the effectively radiated power (ERP) of the transmitter.Īs the propagation distance increases, the radiated energy is spread over the surface of a sphere of radius d, so the power received decreases proportional to d -2. Free Space Path Loss Calculator Free Space Path Loss is used the calculate the attenuation (reduction) of signal strength between two antennas. f cwith c the velocity of light and f c the carrier frequency. Where A is the effective area or `aperture' of the antenna, with G R= 4 p A / l 2. The available power p R at a receive antenna with gain G R is The power density w at distance d from a transmitter with power p Tand antenna gain G tis The surface area of a sphere of radius d is 4 p d 2. This allows us to analyse the effect of distance on the received signal power.įigure: Transmit antenna modelled as a point source. 900 MHz ) (input1) : Mobile Antenna Gain (e.g. Omni-directional antenna is spread over the surface of a sphere. Free Space path loss calculator Enter values as mentioned in the example to calculate free space path loss. We are allowed to model the radiating antenna as a point source with negligible physical dimensions. In particular, the influence of the earth surface is assumed to be entirely absent.įor propagation distances d much larger than the antenna size, the far field of the electromagnetic wave dominates all other components. Note that lambda is equivalent to c/frequency where in c is equal to 3 x 108 in FSL formula.

Neither absorbing obstacles nor reflecting surfaces are considered. Receiver sensitivity In step-1, EIRP is calculated In step-2, Free Space Loss is calculated based on EIRP and receiver sensitivity (Pr) In step-3, coverage distance is calculated based on free space path loss formula. The free space propagation model assumes a transmit antennaĪnd a receive antenna to be located in an otherwise empty environment. Free Space Propagation JPL's Wireless Communication Reference Website Chapter: Wireless Channels


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
